Relevance
The project aims at the development of an integrated risk assessment-based management and warning instrument, contributing to the prevention and reduction of the negative impacts caused by geo-tectonic activity, as earthquakes and tsunamis.
Developing a generic assessment structure with a set of tools that allow the interdisciplinary evaluation of various geophysical risks and the early warning to all involved authorities, research organisations and academic institutes, the project contributes significantly to the priorities of the Information Technology Society as stated in the 2010 initiative. The targets of the project are, further, in conjunction with the Dublin principles stated in 1992, the EU Sustainable Development Strategy as declared in 2001 and the World Summit on Sustainable Development (WSSD) as decided in Johannesburg in 2002.
The project is based on a strongly interdisciplinary approach (earth sciences, natural hazards, ICT background, etc.) strengthening the scientific and technological capacities to contribute to the understanding, the monitoring, the early warning of communities and the preservation of coastal ecosystems.
Relations to the actual discussions of the society
The geological hazards in the past years (see Table B.1: Tsunami: "Indian Ocean", December 26, 2004, off west coast northern Sumatra, Indonesia; and earthquake: "Kashmir", October 8, 2005, Kashmir & N.W.F.P, Pakistan) require the concentration of the scientific capacities, authorities, and further power of the society on the early recognition, alleviation and farsighted repair of the following effects of such hazards. The Table B.1demonstrates the importance of activities for the development of the implementation of a global earthquake and tsunami early warning system.
The EC has recognised the relevance of such events for the society and have launched the activity “Early warning systems for geo-physical hazards” in the Sixth Framework Programme with the Strategic Objective 2.6.5: International Co-operation.
The earth is a dynamic physical system and the earth’s crust is divided into continental-sized, subcontinental and many smaller plates. The causes of geological hazards such as earthquakes and tsunamis are in relation to the inner structure of the earth and the earth’s crust, and especially the continental drift and plate tectonics as is demonstrated in Fig. B2-1 of /Steven L. Kramer, p. 26./. (The figures are presented in Attachment C.0). In the next Figure B2-2 are presented the worldwide seismic activity / Steven L. Kramer, p. 27/. These activities are in close correlation to the plates activities, presented in Figure 2.9.
Most threatening activities in Europe arise in the Mediterranean region. We propose the orientation of our CAEM-activities in relation to one region of Greece – one of the most important seismic risk region in Europe. In Figure B.2-3 /E. Schmid, p. 27/ we present the detailed earthquake hazard map from Greece in a clear manner and give hints for what the high risk regions are, especially on the west coast of Greece.
Very important information is presented by the following EC-project P7: Demonstrating the utility of SAR differential interferometry for the assessment of seismic risk:
“Earthquakes are a major hazard and world-wide there are on average 1,000 deaths per year. In Greece, the cost of damage exceeded 1.2 billion USD in 1995.”
For this reason, Greece will be an excellent European test bed for the development, installation, test and validation of the CAEMS. For this reason we have chosen Prof. Dr. Dr. Geomorphologist Niki Evelpidou, Remote Sensing Laboratory of the University of Athens as Coordinator of the project and have integrated further partners from Greece.
IST-related activities
Innovative methods of the Information and Communication Technologies as is in line with the Priorities and the Strategic Objectives of the FP6-IST-activities open new chances for the design of the CAEMS. Some of the partners of the Network of Excellence CARiMan come from affected regions and can realise close contact to practical application of our solutions.
The activities for the development of the project CAEM are divided into 10 Workpackages as well as the System Architecture – SA - and 6 subsystems. The System Architecture includes the following subsystems in relation to the FP6-IST-strategy:
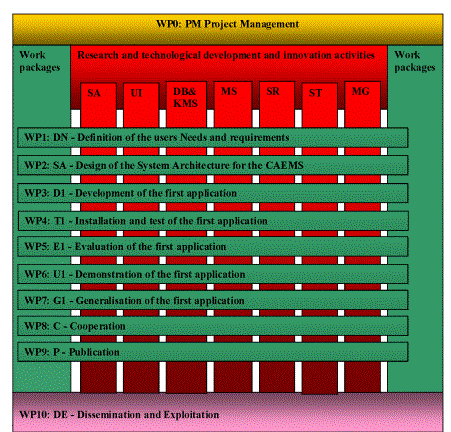
Fig. B2-1: The relation between the Workpackages and the IST related subsystems of CAEMS
UI: User Interface
Intelligent interfaces and surfaces to provide optimal access of the user to innovative computer technologies with natural interaction. The work is centred on multilingual and multicultural access and communication..
DB&KMS: Data Base & Knowledge Management Systems
“This vision of "ambient intelligence" places the user, the individual, at the centre of future developments for an inclusive knowledge-based society for all.” /EC, p. 6/. “Research in the area of environment will focus on knowledge-based systems for natural resource management and for risk prevention and crisis management including humanitarian mine clearance.” /EC, p. 7/. “Work will focus on technologies to support the process of acquiring and modelling, navigating and retrieving, representing and visualising, interpreting and sharing knowledge.” /EC, p. 10/.
MS: MicroSystems for sensors and actuators
The objective is to improve the accuracy, performance and functionality of MicroSystems for high accuracy signal acquisition, amplification and digitalisation. However MicroSystems are designed and used for the outline of further components of the CAEMS. The project will stimulate the development and application of high accuracy and cheap sensor technology for distributed applications in earth management.
SR: Signal Recognition
The signal analysis and recognition is realised on the basis of established and optimised procedures. Here we use state of the art algorithms for signal analysis and recognition. At the centre of the R&D-activities in this subsystem are the development, adaptation, and application of the procedures of the Virtual Sources - VQ – as a Humanlike Perception System.
ST: Signal Transmission
High performance, secure and innovative signal transmission technology is used for the transmission of the signals from the sensors to the central station as well as the user-computer communication. The application of the next generation of mobile and wireless systems is preferred.
International integration of the R&D-activities
The
proposed R&D-activities are fully integrated in international and especially
European R&D activities. A consortium of about
high-ranked international experts are integrated (www.ICSRoscher.de/CARiMan.htm).
The Joint Programme of Activities of CARiMan include the special JPA: Seismic
CARiMan and was the basis for the design of the CAEM consortium. The proposal
for the development of the CAEMS is in line with the FP6-IST-Call 6, Strategic
Objective: 2.6.5: International Co-operation,
in the field of early warning systems for geo-physical hazards. We have further invited more than 100 international experts in the field of geological hazards around to world for cooperation as the basis for the WP8: Cooperation (see Attachment C3). These experts will be integrated as advisers and knowledge distributors from the beginning.