|
ICS Dr. G.
Roscher GmbH
|
HeartScope
|
 Heart-circulation-disease
is a civilization disease with a high risk of fatality especially in
industrial regions like Europe. At the same time, such industrialized
regions exhibit frequently high unemployment patterns coupled with
stress related syndromes on the persons considered which might
contribute to such diseases. This is the motivation for innovative
product development using national and international co-operation to
overcome unemployment on the one hand and to recognize persons under
increased health risk on the other.
Heart-circulation-disease
is a civilization disease with a high risk of fatality especially in
industrial regions like Europe. At the same time, such industrialized
regions exhibit frequently high unemployment patterns coupled with
stress related syndromes on the persons considered which might
contribute to such diseases. This is the motivation for innovative
product development using national and international co-operation to
overcome unemployment on the one hand and to recognize persons under
increased health risk on the other.
The
real-time recognition of the electrical activities of the heart,
known as the electrocardiogram (ECG), is a unique feature of the
developed system which uses powerful information technologies as its
technical basis for continuous monitoring of patients at risk, and
recognizes critical situations in real-time with highest accuracy. In
addition, state-of-the-art communication technologies are also used
for the transmission of relevant data to present the risk situation
of the patient to a qualified physician for making decisions. The
scientific background for this work is related to the project
"Methods of Nonlinear Dynamic for analysis of the ECG, for risk
stratification and therapy assessment for heart patients",
supported by the German Ministry
of Education and
Research (Grant 13N7129).
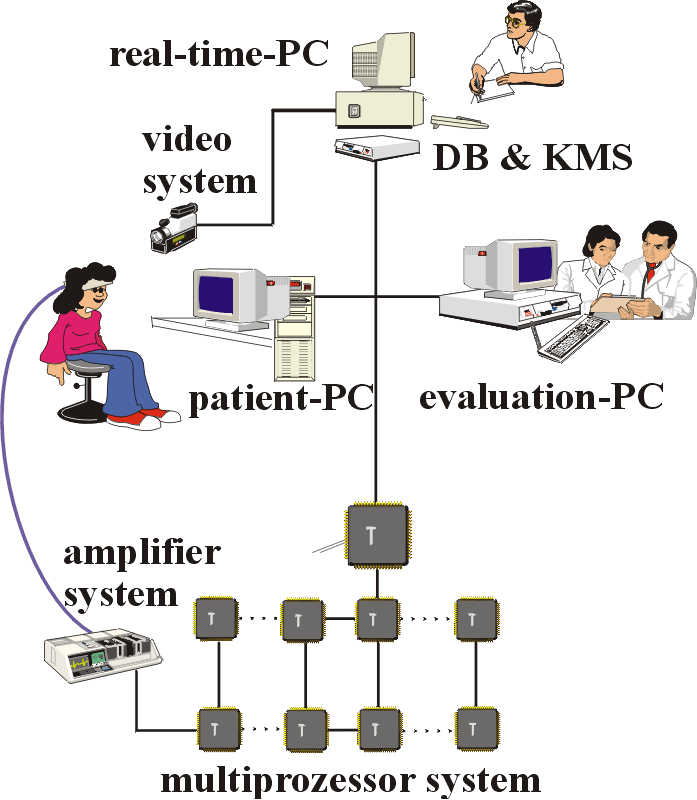
The
ECG system HeartScope consists of a special amplifier system
for high quality signal detection in open field conditions. A high
performance multi-processor system which is capable of processing the
huge amounts of data produced by a multichannel ECG record to gain
information in real-time has also been developed. Algorithms for
recognition of events in single channels are implemented in the first
level of the multi-processor system. We use high performance image
processing algorithms in the second level, interpreting the sampled
values of each channel as pixels of the image, 256 up to 2.000 times
per second. This new and patented method is based on information
theory and describes the ECG activity as sequences of so called
virtual sources in parameters of amplitude, time and space.
Fuzzy
logic and methods of AI are used to define and recognise sequences of
virtual sources as QRS-complexes or heart beats in real-time. The
network of two or more Personal Computers (PC's) is co-ordinated
through the multi-processor system for presentation of ECG activity
and controlling. These methods are integrated into the powerful
graphic user interface and uses a database system. Incorporated into
this user interface are state of the art algorithms from the NIMH
(Washington / USA) for mappings, FFT, etc.
The innovative method for
the real-time recognition of signals worked - in contrast to the
established frequency domain methods such as the Discrete Fourier
Transform (DFT) - in the time domain. This new method is
based on the “old” peak measurement and evaluates each
event in the signal.
Each event is
transformed into a data structure named Virtual
Source (in German: Virtuelle
Quelle –
VQ). The
result of this transformation is the description of the signal as a
sequence of VQs. Further steps build up a hierarchical system of
chained lists of VQs.
This description of
the signal can be easily manipulated by mathematical methods and can
be easily recognized.
This high performance
requires the application of time domain methods for signal
recognition of the highest accuracy, which employs the latest
technologies in the fields of Data Base (DBS) and Knowledge
Management Systems (KMS). Each incoming signal is stored in the
DBS. These signals are transformed in the VQs, segmented and
indexed by the time and by the segment number. The classification is
achieved using DB&KMS for the acquisition of personal knowledge
in direct communication between the user and the DB&KMS.
Publication
HeartScope
PatiMon
CARiMan
Herz
EKGNLD
 Heart-circulation-disease
is a civilization disease with a high risk of fatality especially in
industrial regions like Europe. At the same time, such industrialized
regions exhibit frequently high unemployment patterns coupled with
stress related syndromes on the persons considered which might
contribute to such diseases. This is the motivation for innovative
product development using national and international co-operation to
overcome unemployment on the one hand and to recognize persons under
increased health risk on the other.
Heart-circulation-disease
is a civilization disease with a high risk of fatality especially in
industrial regions like Europe. At the same time, such industrialized
regions exhibit frequently high unemployment patterns coupled with
stress related syndromes on the persons considered which might
contribute to such diseases. This is the motivation for innovative
product development using national and international co-operation to
overcome unemployment on the one hand and to recognize persons under
increased health risk on the other.